DVI-D Vs. DVI-I Connector: Side-By-Side Comparison
A DVI connection is common. It comes in multiple types, with DVI-D and DVI-I being among the most popular options. This article will give you a side-by-side comparison between the DVI-D vs. DVI-I. Let’s see how they differ!
What Is The Difference Between DVI-D Vs. DVI-I?
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) connectors, along with DisplayPort and HDMI connections, are common on GPUs. They are often white ports on your GPU.
The DVI connection uses a digital protocol to transfer binary data representing pixel illumination. It will transmit each number when a panel works in its original resolution. Then, the monitor can set the proper brightness for every pixel.
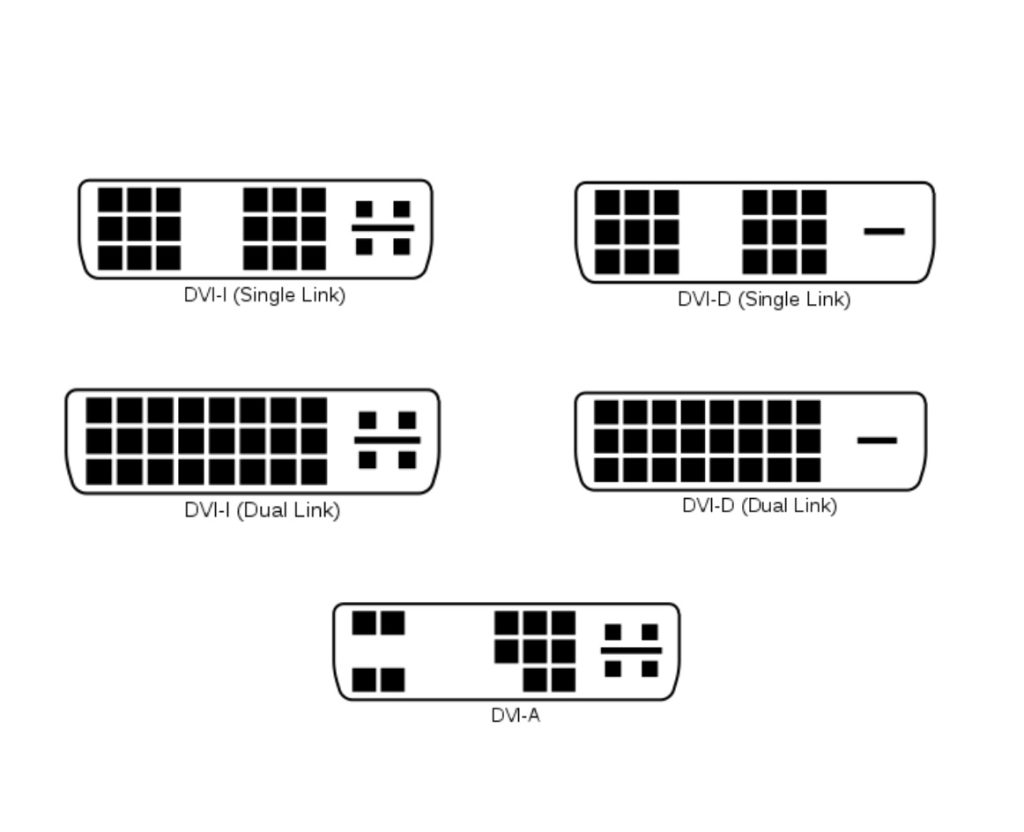
There are three types of DVI connectors: DVI-A, DVI-D, and DVI-I. Besides, DVI-I and DVI-D have two versions, single-link and dual-link connectors.
DVI-I (with I meaning Integrated) is the connector that can transmit both analog and digital signals. On the other hand, DVI-D (Digital) can’t handle analog signals.
Here are the similarities and differences between DVI-D and DVI-I:
|
DVI-D |
DVI-I | |
|
Transmission |
Digital signals |
Digital and analog signals |
|
Pins |
Single-link: 19 pins |
Single-link: 23 pins |
|
Displays |
Only LED-backlit LCD |
CRT and LED-backlit LCD monitors |
|
Resolution |
Single-link: 1920 x 1200 |
Single-link: 1920 x 1200 |
Similarities
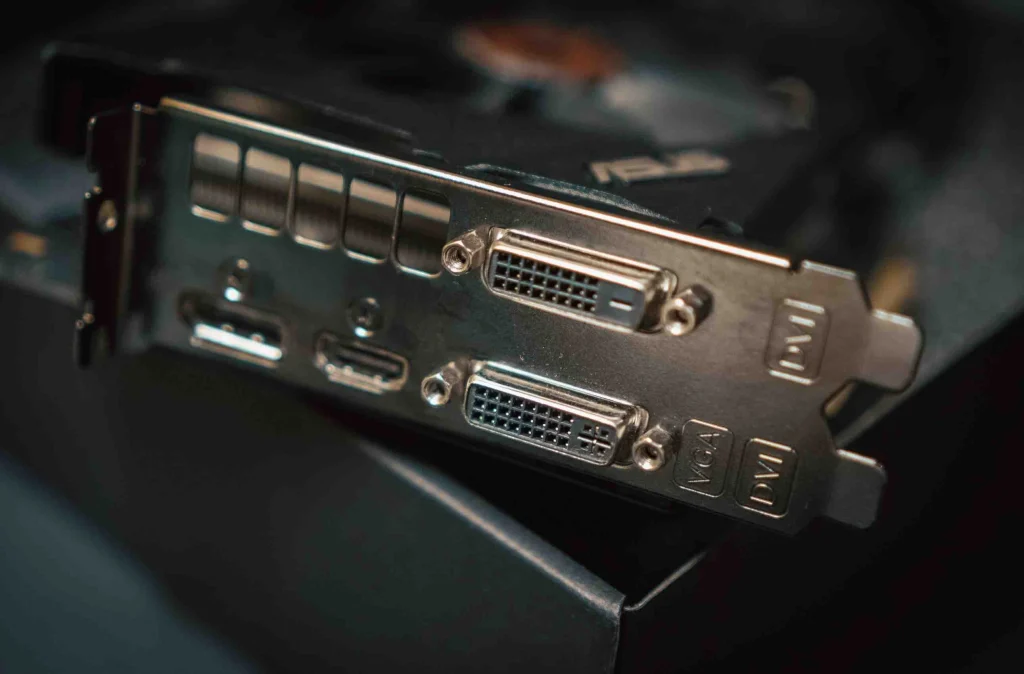

Because they are both DVI connectors, DVI-D and DVI-I share many features in common. For example:
- They both deliver high-definition digital video from your computer to the monitor.
- They can handle data at high speed to ensure a stable and smooth playback.
- You can use them for digital displays, like LCD monitors.
- They are common in computers, so most computer manufacturers support them.
Differences
Aside from the noticeable similarities above, DVI-D and DVI-D are different from each other in these factors:
- DVI-I allows both digital and analog data, whereas DVI-D only supports digital signals.
- All the pins needed for a single-link DVI cable are available on DVI-I connections, but DVI-D connectors don’t have the extra four pins needed to carry the analog signals.
- The tall, flat pin on DVI-D is shorter than on DVI-I.
- The single-link of DVI-I connections come with 23 pins, while there are only 19 pins in the single-link DVI-D.
- There are 25 pins and 29 pins in dual-link DVI-D and DVI-I, respectively.

You may wonder about the difference between DVI single-link and dual-link. In fact, the maximum resolution and data lanes will set them apart.
A single-link connector has only one data lane, while the dual-link version has two. The additional lane enables it to transmit more signals and handle higher resolutions.
In addition, a single-link DVI connector can only support the highest resolution of 1920 x 1200, whereas you can use the dual-link DVI for resolutions of up to 2560 x 1600.
Which Is Better: DVI-D or DVI-I?
Your decision depends on your specific requirements and the type of display you have. Here are some things to think about when choosing between DVI-I and DVI-D:
- Type of display: DVI-D is the best option if all your displays are digital, such as LCD and flat-panel monitors. However, if you need a combination of analog and digital displays, go for the DVI-I.
- Compatibility: DVI-D is only compatible with digital displays. Meanwhile, DVI-I is more flexible since you can use it with both analog and digital displays.
- Budget: If all your monitors are digital, using DVI-D might save you money because DVI-I costs more than DVI-D.
Can You Turn A DVI-I Into A DVI-D?
No. The connection design determines the difference between these connectors, not the software settings or cable management.
While DVI-D connections only have digital pins, DVI-I connectors feature analog and digital pins. Essentially, you can’t change the DVI-I connector’s maximum number of pins or allowed signal types.
You can ignore the analog pins if you use DVI-I for a digital display. However, converting DVI-I into DVI-D is impossible.
Comparison Table: DVI-A, DVI-D, DVI-I Connector Types
| DVI Type | Connector | Signal Type | Max Resolution | Bandwidth |
| DVI-D Single Link |
 |
Digital | 1920 X 1080 | 4.59 Gbps |
| DVI-D Dual Link |
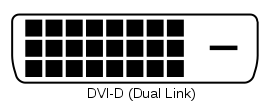 |
Digital | 2560 x 1600 | 9.9 Gbps |
| DVI-I Single Link |
 |
Digital/Analog | 1600 X 1200 | 4.95 Gbps |
| DVI-I Dual Link |
 |
Digital/Analog | 2560 x 1600 | 9.9 Gbps |
| DVI-A Analog |
 |
Analog | 1920 X 1080 |
Pete is a software engineer who currently works full-time managing OMGMonitor.com. On the side, he enjoys coding his own projects and spending time with his wife and two dogs. When he's not working or hanging out with family and friends, you can find him playing the guitar or running. My Instagram.